Network Integration
IBM QRadar and Splunk
IBM QRadar and Splunk are both leading Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) solutions that help organizations monitor, detect, and respond to security threats and incidents.
Here are key aspects of an overview for each solution:
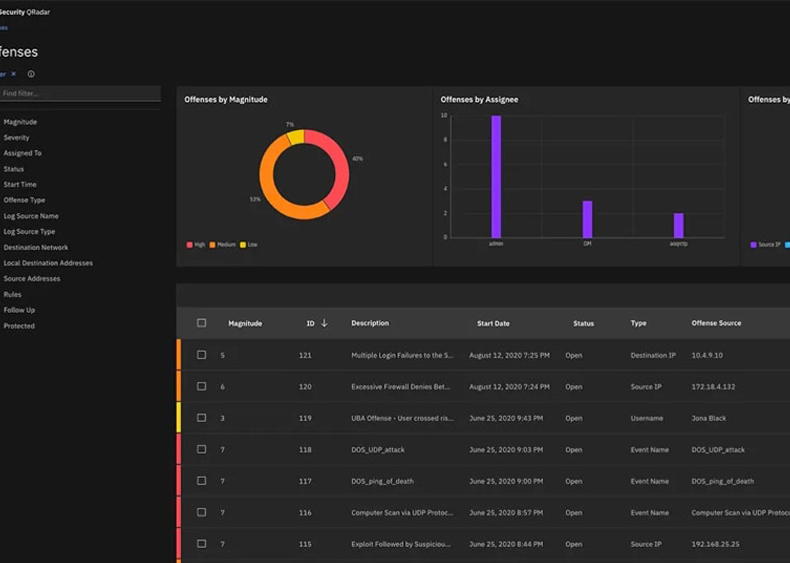
- Vendor: IBM QRadar is developed and offered by IBM.
- Functionality: IBM QRadar is a comprehensive SIEM solution that provides real-time monitoring and analysis of security events and incidents. It collects data from various sources across an organization's IT infrastructure, including logs, network flows, and threat intelligence feeds.
- Integration: IBM QRadar integrates with various security technologies and third-party solutions, allowing organizations to enhance their security posture by connecting different data sources and tools.
- Scalability: QRadar is designed to scale to the needs of large enterprises and is suitable for organizations with complex and extensive IT environments.
-
Features:
- Log Management: QRadar collects and stores logs from a wide range of devices and applications for forensic analysis and compliance reporting.
- Threat Detection: It employs advanced analytics and machine learning to identify and prioritize potential security threats.
- Incident Response: QRadar helps security teams investigate and respond to security incidents more effectively.
- Compliance Reporting: It assists organizations in meeting regulatory compliance requirements by providing predefined reports and alerts.
- Vulnerability Management: QRadar can integrate with vulnerability assessment tools to correlate vulnerabilities with threats.
Splunk:
- Vendor: Splunk is a leading data analytics and machine data platform provider, and it offers Splunk Enterprise Security as its SIEM solution.
- Functionality: Splunk Enterprise Security is a SIEM solution that uses the Splunk platform for log and event data collection, analysis, and visualization. It is known for its flexibility and extensibility.
- Integration: Splunk's strength lies in its ability to integrate with a wide range of technologies and applications, both in the security domain and beyond.
- Scalability: Splunk Enterprise Security can scale to meet the requirements of large enterprises and is known for its adaptability to diverse IT environments.
-
Features:
- Data Collection: Splunk Enterprise Security can collect and index data from virtually any source, making it highly adaptable to an organization's needs.
- Threat Detection: It provides customizable threat detection and alerting capabilities.
- Incident Investigation: Splunk offers powerful search and analytics capabilities, making it useful for in-depth investigations.
- Compliance: It helps organizations address compliance requirements with custom reporting and visualization tools.
- Machine Learning: Splunk utilizes machine learning for anomaly detection and predictive analytics.
Comparison:
- IBM QRadar is a specialized SIEM solution with a strong focus on security, while Splunk is a broader data analytics platform that includes a SIEM module (Splunk Enterprise Security).
- QRadar is known for its out-of-the-box threat detection capabilities, making it a good choice for organizations looking for a turnkey SIEM solution. Splunk, on the other hand, is highly customizable and adaptable.
- Splunk's versatility makes it suitable for a wide range of data analytics and monitoring use cases beyond security.
Ultimately, the choice between IBM QRadar and Splunk as a SIEM solution depends on an organization's specific requirements, existing infrastructure, and preferred approach to data analytics and security monitoring. Both solutions are highly respected in the industry and can be effective tools for strengthening an organization's security posture.

Endpoint Security Solutions
Endpoint security solutions are critical for protecting an organization's network and data by securing individual devices, such as computers, smartphones, and tablets, that connect to the network. These solutions are designed to defend against a wide range of threats, including malware, ransomware, phishing attacks, and insider threats.
Here are key components and features of an endpoint security solution:
- Antivirus and Anti-Malware: The core of any endpoint security solution is antivirus and anti-malware protection. It scans files and applications for known malware signatures and behavior patterns, preventing malicious software from infecting the device.
- Firewall: An integrated firewall monitors network traffic and blocks unauthorized access to the device. It helps protect against network-based attacks and intrusion attempts.
- Behavioral Analysis: Many modern endpoint security solutions employ behavioral analysis to identify and stop previously unknown threats based on suspicious activities and behavior patterns, rather than relying solely on known signatures.
- Sandboxing: Some solutions use sandboxing to isolate and execute suspicious files or applications in a controlled environment to analyze their behavior without risking damage to the device.
- Email and Web Protection: Endpoint security solutions often include email filtering and web protection features to block phishing emails, malicious websites, and other online threats.
- Device Control: Device control features allow administrators to manage and restrict the use of external devices, such as USB drives, to prevent data leaks or the introduction of malware.
- Encryption: Endpoint encryption protects sensitive data on devices by encrypting it, making it unreadable without the appropriate decryption key. This is particularly important for laptops and mobile devices.
- Patch Management: Ensuring that the operating system and software on endpoints are up-to-date with the latest security patches is crucial. Some endpoint security solutions include patch management features to automate this process.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP): DLP features help organizations monitor and control the movement of sensitive data on endpoints to prevent data breaches and leaks.
- Centralized Management: A centralized console allows administrators to manage and monitor all endpoint security activities from a single location, making it easier to enforce security policies and respond to threats.
- Incident Response and Reporting: Endpoint security solutions provide incident response capabilities to investigate and remediate security incidents. They also offer reporting tools to generate compliance reports and analyze security trends.
- Machine Learning and AI: Many advanced endpoint security solutions incorporate machine learning and artificial intelligence to detect and respond to evolving threats more effectively.
- Integration: Integration capabilities with other security solutions, such as SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) systems and threat intelligence feeds, enable a more comprehensive security posture.
Choosing the right endpoint security solution for an organization depends on factors like the size of the network, the diversity of devices, compliance requirements, and the budget. It's essential to select a solution that provides comprehensive protection while allowing for efficient management and scalability to meet evolving security needs.
Sophos Firewall
Sophos is a well-known cybersecurity company that offers a range of security solutions, including firewalls. A Sophos firewall is designed to protect an organization's network infrastructure by monitoring and controlling incoming and outgoing network traffic based on an organization's previously established security policies.
Here are key aspects of a Sophos firewall:

- Unified Threat Management (UTM): Sophos firewalls often provide UTM capabilities, which means they combine various security features into a single device. These features may include firewalling, intrusion prevention, antivirus and anti-malware protection, web content filtering, and application control.
- Next-Generation Firewall (NGFW): Sophos also offers NGFWs, which go beyond traditional firewalls by providing advanced features such as deep packet inspection, SSL inspection, and the ability to identify and control applications and users.
- Security Policies: Administrators can define and enforce security policies on a Sophos firewall. These policies dictate how traffic is handled, including which applications are allowed or blocked, which websites can be accessed, and what security measures are applied to incoming and outgoing data.
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention (IDS/IPS): Sophos firewalls can detect and prevent network intrusions and attacks. They analyze network traffic patterns to identify and block suspicious or malicious activity.
- Web Filtering: Sophos firewalls often include web content filtering capabilities, allowing organizations to restrict access to websites based on categories, URLs, or keywords. This helps improve security and productivity.
- Application Control: Sophos firewalls can identify and control specific applications and services running on the network. This feature helps organizations manage bandwidth usage and enforce security policies.
- VPN Support: Many Sophos firewalls support Virtual Private Networks (VPNs), enabling secure remote access to the organization's network resources. This is useful for remote workers or branch offices.
- Reporting and Logging: Sophos firewalls provide reporting and logging capabilities, allowing administrators to monitor network activity, track security incidents, and generate compliance reports.
- High Availability: Sophos offers options for high availability and redundancy to ensure uninterrupted network security even in the event of hardware failures.
- Cloud Management: Some Sophos firewalls can be centrally managed through a cloud-based platform, simplifying deployment and management for organizations with multiple locations.
- Integration: Sophos firewalls can integrate with other Sophos security solutions, such as endpoint protection and email security, to provide a coordinated and layered defense against cyber threats.
Sophos firewalls are suitable for a wide range of organizations, from small businesses to large enterprises, looking to enhance their network security and protect against modern cyber threats. They offer a comprehensive set of security features and can be customized to meet the specific security needs and compliance requirements of each organization.

Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR)
Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) is a cybersecurity solution designed to detect and respond to advanced threats and security incidents on individual endpoints, such as computers, servers, and workstations. EDR solutions provide real-time monitoring, threat detection, and automated response capabilities to enhance an organization's overall security posture.
Here are key aspects and features of an EDR solution:
- Real-Time Monitoring: EDR solutions continuously monitor endpoint activities and behaviors to detect anomalous or suspicious actions. They capture detailed telemetry data, including process execution, file changes, network connections, and user interactions.
- Threat Detection: EDR solutions leverage advanced analytics, machine learning, and behavioral analysis to identify potential threats, including malware, ransomware, insider threats, and zero-day attacks. They compare observed behaviors to known threat patterns and baselines.
- Incident Investigation: When a security incident is detected, EDR solutions provide extensive investigation capabilities. Security teams can drill down into endpoint data, conduct forensics, and trace the origin and scope of an attack.
- Alerting and Prioritization: EDR solutions generate alerts based on detected threats, ranking them by severity and providing contextual information. This helps security teams prioritize their response efforts.
- Automated Response: EDR solutions often offer automated response actions to contain and mitigate threats. These actions can include isolating the affected endpoint from the network, terminating malicious processes, and rolling back system changes.
- Behavioral Analysis: Behavioral analytics is a core component of EDR solutions. They establish a baseline of normal endpoint behavior and raise alerts when deviations occur, potentially indicating a security incident.
- Threat Intelligence Integration: EDR solutions integrate with threat intelligence feeds and databases to enrich threat context and enable proactive threat hunting.
- Centralized Management: A centralized management console allows security teams to oversee and configure EDR policies, monitor alerts, and initiate responses across all endpoints in the network.
- Forensic Data Collection: EDR solutions store detailed endpoint telemetry data, providing a historical record of endpoint activity. This data is invaluable for post-incident investigations and compliance reporting.
- Integration with Security Ecosystem: EDR solutions can integrate with other security technologies, such as SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) systems, firewalls, and antivirus solutions, to provide a holistic security defense.
- Reporting and Compliance: EDR solutions offer reporting capabilities that facilitate compliance reporting and provide insights into security incidents and trends.
- Endpoint Visibility: EDR solutions provide comprehensive visibility into endpoint assets, including hardware and software inventory, enabling organizations to maintain accurate asset management.
Selecting the right EDR solution depends on factors such as an organization's size, industry, compliance requirements, and budget. It's essential to choose an EDR solution that aligns with an organization's security needs and integrates seamlessly with its existing security infrastructure to create a robust defense against evolving threats
Fortinet Firewall
Fortinet is a prominent cybersecurity organization recognized for its FortiGate series of firewalls. A Fortinet firewall is meticulously engineered to safeguard networks against a diverse spectrum of cybersecurity threats, meticulously monitoring and controlling both inbound and outbound network traffic.
Here are the key attributes and features associated with Fortinet firewalls:

- Unified Threat Management (UTM): Fortinet firewalls consistently feature Unified Threat Management (UTM) capabilities, consolidating a multitude of essential security functions within a singular device. These encompass traditional firewall functions, intrusion prevention, robust antivirus and anti-malware defenses, comprehensive web content filtering, and meticulous application control.
- Next-Generation Firewall (NGFW): Fortinet's Next-Generation Firewalls (NGFWs) transcend the confines of traditional firewalls, offering advanced functionalities such as deep packet inspection, SSL/TLS inspection, and the discernment and control of applications and users.
- Security Policies: Fortinet firewalls empower administrators to formulate and implement precise security policies. These policies dictate the treatment of network traffic, including the authorization or prohibition of specific applications, permissible website access, and the enforcement of security measures on transmitted data.
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention (IDS/IPS): Fortinet firewalls are equipped with robust Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS) to detect and mitigate network intrusions and cyberattacks. They discern irregularities in network traffic patterns, thereby identifying and obstructing suspicious or malicious activities.
- Web Filtering: Fortinet firewalls often encompass sophisticated web content filtering functionalities. These features permit organizations to impose access restrictions on websites based on pre-defined categories, URLs, or specific keywords, thus enhancing both security and productivity.
- Application Control: Fortinet firewalls excel at pinpointing and managing individual applications and services operating within the network. This level of granularity allows organizations to optimize bandwidth usage and enforce security protocols with precision.
- Virtual Private Network (VPN) Support: Fortinet offers resilient VPN capabilities, guaranteeing secure remote access to an organization's network resources. This capability is invaluable for remote employees and branch offices.
- Logging and Reporting: Fortinet firewalls boast comprehensive logging and reporting functionalities. Administrators benefit from the ability to scrutinize network activities, investigate security incidents, and generate compliance reports efficiently.
- High Availability: Fortinet provides a suite of high-availability solutions, ensuring uninterrupted network security even in the face of hardware failures. These solutions include active-passive and active-active clustering.
- Integration: Fortinet firewalls readily integrate with other Fortinet security solutions, such as endpoint protection, email security, and Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems. This integration fosters a holistic and coordinated defense against dynamic cybersecurity threats.
- Scalability: Fortinet firewalls are available in diverse models, catering to the requirements of small businesses, enterprises, and service providers. They can be readily scaled to meet evolving needs.
- Fortinet Security Fabric: Fortinet champions the concept of a Security Fabric, an integrated and collaborative approach to cybersecurity. It enables various Fortinet security products to exchange threat intelligence and respond in real-time to emerging threats.
Fortinet Firewalls are widely adopted by organizations of varying sizes, serving as a linchpin in their network security strategy. They offer an exhaustive suite of security features and can be meticulously tailored to adhere to specific security mandates and regulatory compliance standards. Fortinet's commitment to continuous research and threat intelligence ensures that their firewalls remain a stalwart defense against the ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats.